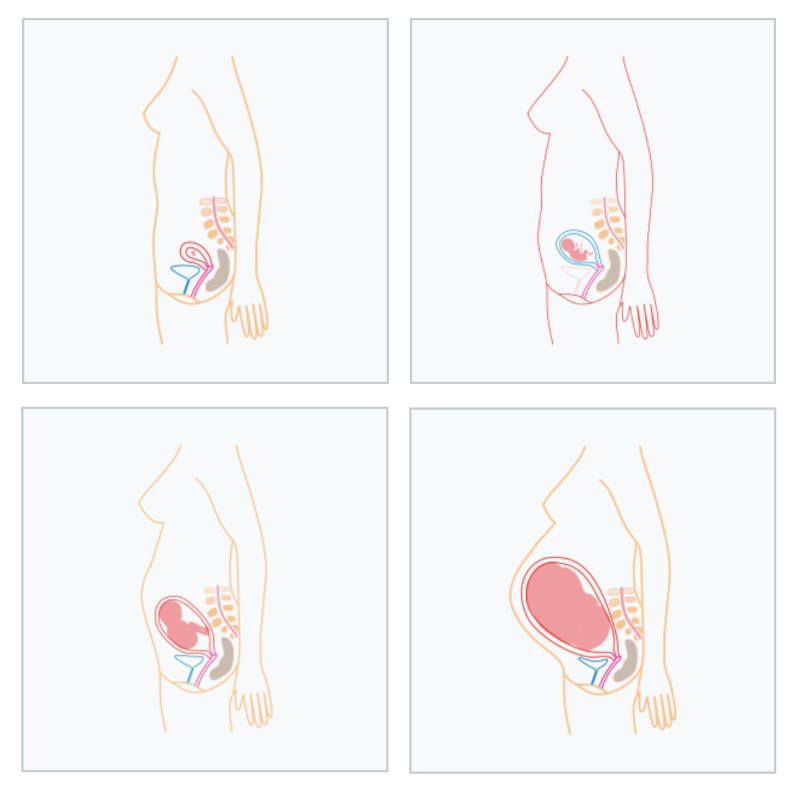
A typical pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks, or around 9 months, from the first day of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP) to the birth of the baby. This period is usually divided into three trimesters:
1. First trimester: Weeks 1 to 12
2. Second trimester: Weeks 13 to 26
3. Third trimester: Weeks 27 to birth
Each trimester marks specific stages of fetal development and maternal changes.
The development of the fetus and changes in the mother’s body during each of the 40 weeks of pregnancy are quite detailed. Here's an overview by trimester:
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
Weeks 1-4:
- Fertilization: The sperm fertilizes the egg, forming a zygote.
- Implantation: The zygote travels down the fallopian tube and implants itself into the uterine wall, becoming an embryo.
- Early Development: The embryo begins to develop essential structures, including the amniotic sac, placenta, and umbilical cord.
Weeks 5-8:
- Organ Formation: The heart begins to beat, and major organs such as the brain, spinal cord, and intestines start to develop.
- Limb Buds: Small buds that will become arms and legs start to form.
- Facial Features: Basic facial features, including the eyes and ears, begin to develop.
Weeks 9-12:
- Fetal Stage: The embryo is now called a fetus.
- Movement: The fetus begins to move, although it is too small for the mother to feel it.
- Growth: The fetus continues to grow, and by the end of the first trimester, it is about 2.5 inches long.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-26)
Weeks 13-16:
- Sensory Development: The fetus's eyes and ears continue to develop, and it can start to hear sounds.
- Hair and Nails: Hair, eyelashes, and nails begin to grow.
- Movements Felt: The mother may start to feel the baby move, often described as "quickening."
Weeks 17-20:
- Growth: The fetus grows rapidly and starts to develop fat under the skin.
- Gender: The gender of the baby can often be determined via ultrasound.
- Heartbeat: The fetal heartbeat can be heard with a stethoscope.
Weeks 21-26:
- Taste Buds: Taste buds develop, and the fetus can begin to taste amniotic fluid.
- Lungs: The lungs start to produce surfactant, which is essential for breathing after birth.
- Vernix Caseosa: The skin is covered with a protective, waxy coating called vernix caseosa.
Third Trimester (Weeks 27-40)
Weeks 27-30:
- Brain Development: The brain grows rapidly, increasing in complexity.
- Muscle and Fat: The fetus continues to gain muscle and fat, preparing for life outside the womb.
Weeks 31-34:
- Reflexes: Reflexes such as sucking and swallowing develop.
- Positioning: The fetus often moves into a head-down position in preparation for birth.
Weeks 35-37:
- Final Growth: The fetus continues to grow, putting on the final layers of fat.
- Lungs Mature: The lungs continue to mature and prepare for breathing after birth.
Weeks 38-40:
- Full Term: The fetus is considered full-term at 39 weeks.
- Birth Preparation: The body prepares for labor, and the baby moves lower into the pelvis.
- Delivery: The baby is born around week 40, although full-term pregnancies can naturally vary by a week or two.
Each pregnancy is unique, so the timing and specific developments can vary slightly from one pregnancy to another.
Try these pregnancy calculation tools:
Conception Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
Due Date Calculator