Blog
How does GPS calculate distances
GPS (Global Positioning System) calculates distances using a technique called trilateration, which relies on precise measurements of time and the speed of light. Here's how it works:
How far is a light-year?
A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year in a vacuum. It's a unit of length used in astronomy to measure vast distances across space. Light travels at a speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second in a vacuum. So, over the course of one year, light covers a distance of roughly 9.461 trillion kilometers (or about 5.879 trillion miles). This immense distance helps astronomers measure distances between stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects in the universe.
The metric system vs. Imperial system: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Impact on Society
The debate between the metric system and the Imperial system is complex, and opinions vary on whether one system makes the world better or leads to confusion. Here are some arguments for both sides:
Metric System:
How long is a nanometer
A nanometer is a unit of length equal to one billionth of a meter, or 0.000000001 meters. To put it in perspective, a nanometer is incredibly small. For example, the width of a DNA double helix is approximately 2 nanometers, and the diameter of a typical virus particle ranges from about 20 to 400 nanometers. Nanotechnology deals with structures and devices on the scale of nanometers, showcasing the precision and minuteness of this unit of measurement.
What is a meter and how is it defined
A meter is a fundamental unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). It is used to measure distances, lengths, heights, and widths in various contexts, from everyday activities to scientific research.
The meter is defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum during a time interval of 1/299,792,458 of a second. This definition was established in 1983 by the 17th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) to replace the previous definition based on a physical prototype.
1800 年代的銀行支票是什麼樣子
在浩瀚的歷史長河中,不起眼的銀行支票見證了金融交易的演變。 回到 19 世紀初,當時墨水羽毛筆在羊皮紙上翩翩起舞,交易以優雅的簽名來密封。 想像一下這個場景:1815 年 1 月 31 日,美國歷史上舉足輕重的人物安德魯傑克森 (Andrew Jackson) 坐在辦公桌前。 他有目的地填寫了一張從納許維爾銀行寄給貝內特史密斯的支票,而貝內特史密斯的故事已經被載入史冊。
這張支票,既簡單又深刻的文件,見證了金融交易的基本要素。 從本質上講,它與我們今天所認識的組件相呼應,儘管具有迷人的古老性。 收款人行與現代收款人行類似,指定資金的接收者。 在這種情況下,貝內特史密斯的名字被精心刻上,這是對債務和信任的認可。
轉向美元框(交易價值的數位表示),我們遇到了熟悉的景象。 然而,這些數字本身卻具有一種引力,一種似乎超越了單純貨幣的重量。 在這裡,632.71 美元是財富的證明,在這個每一分錢都蘊含巨大價值的時代,這筆錢足以值得記錄。
但也許這個過去的遺跡最迷人的方面在於用文字表達的數量。 支票用華麗的語言表明了它的意圖:“六百三十二美元七十一美分。” 這是一種語言之舞,一種對價值的詩意詮釋,與現代數字符號的枯燥精度形成鮮明對比。
1800 年代的银行支票是什么样子
在浩瀚的历史长河中,不起眼的银行支票见证了金融交易的演变。回到 19 世纪初,当时墨水羽毛笔在羊皮纸上翩翩起舞,交易以优雅的签名来密封。想象一下这个场景:1815 年 1 月 31 日,美国历史上举足轻重的人物安德鲁·杰克逊 (Andrew Jackson) 坐在办公桌前。他有目的地填写了一张从纳什维尔银行寄给贝内特·史密斯的支票,而贝内特·史密斯的故事已经被载入史册。
支票是一份既简单又深刻的文件,见证了金融交易的基本要素。从本质上讲,它与我们今天所认识的组件相呼应,尽管具有迷人的古老性。收款人行与现代收款人行类似,指定资金的接收者。在这种情况下,贝内特·史密斯的名字被精心刻上,这是对债务和信任的认可。
转向美元框(交易价值的数字表示),我们遇到了熟悉的景象。然而,这些数字本身却具有一种引力,一种似乎超越了单纯货币的重量。在这里,632.71 美元是财富的证明,在这个每一分钱都价值巨大的时代,这笔钱足以值得记录。
但也许这个过去的遗迹最迷人的方面在于用文字表达的数量。支票用华丽的语言表明了它的意图:“六百三十二美元七十一美分。” 这是一种语言舞蹈,一种对价值的诗意诠释,与现代数字符号的枯燥精确形成鲜明对比。
What does a bank check look like in 1800s
In the vast tapestry of history, the humble bank check stands as a testament to the evolution of financial transactions. Journey back to the early 19th century, a time when the ink quill danced upon parchment, and transactions were sealed with the elegant flourish of a signature. Imagine the scene: it's January 31, 1815, and Andrew Jackson, a figure of great prominence in American history, sits at his desk. With purposeful strokes, he fills out a check from the Nashville Bank to Bennett Smith, an individual whose story is lost to the annals of time.
什麽是弧度(rad)
弧度,以符號 rad 表示,是國際單位制 (SI) 中的角度單位,也是許多數學領域中廣泛使用的角度測量標準。
設想一個圓,其圓心位於 O 點,經過圓心到圓上一點的繪製半徑,便可形成一條圓弧。 角度θ(以弧度為單位)是當圓弧長度等於圓的半徑時所形成的角度。
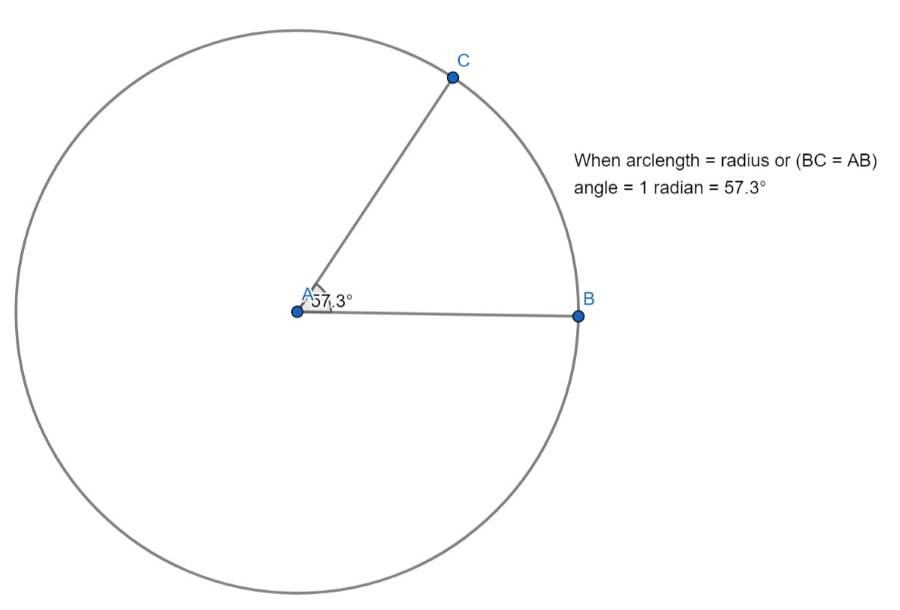
- 若圓弧長度等於半徑 (r),則 θ 為 1 弧度。
- 若弧長是半徑 (2r) 的 2 倍,則 θ 是 2 弧度。
- 依此類推,若弧長是半徑 (nr) 的 n 倍,則 θ 是 n 弧度。
以度為單位時,1 弧度約 57.3 度。 因此,一個完整的圓,360 度,相當於 2π 弧度,因為圓的周長是 2π 乘以其半徑。